My Network
Apr 10, 2010
Cell Phones May Effect Your Sperm
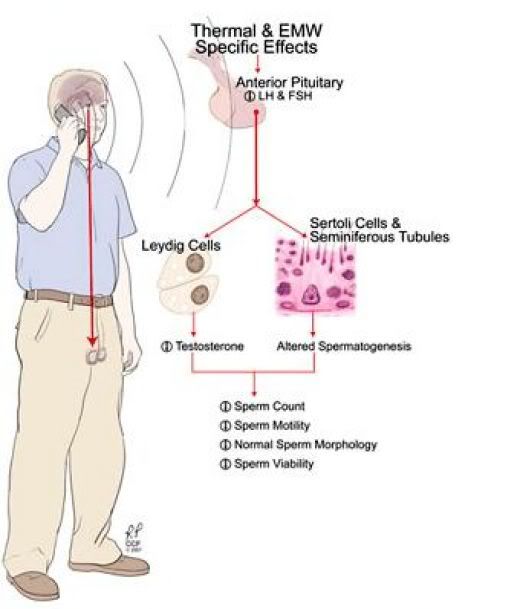 The next time your cell phone rings you just may not want to answer it. A 2008 study conducted at the Cleveland Clinic and published in Fertility and Sterility looks at the effect of cell phone use on various markers of semen quality.
The next time your cell phone rings you just may not want to answer it. A 2008 study conducted at the Cleveland Clinic and published in Fertility and Sterility looks at the effect of cell phone use on various markers of semen quality.The researchers compiled data on 361 male subjects. They evaluated sperm samples on eight different quality parameters: average sperm count, liquefaction time, pH, viscosity, volume, motility, viabiity, and percentage of normal morphology. The participants were then divided into four groups depending on their average daily cell phone usage.
Researchers found that as daily cell phone use increased a decrease was seen in average sperm count, motility, viablilty, and normal morphology--four of the eight markers used to measure semen quality. This study was based on previous research of the effects of electromagnetic waves (EMV) in animal studies that suggested a wide-range of damaging effects on testicular function and the male germ line and reports that showed an effect of cell phone usage on sperm motility in humans.
However, the authors of this study are careful to point out that cell phones operate between 400 MHz and 2000 MHz frequency bands and no attempt was made to study the effects of higher frequencies on semen quality. In addition, although their results indicate a strong associate they do not prove a cause-and-effect relationship.
The authors are continuing their research with a follow-up study that assess a larger group of men and will also account for the effects of lifestyle habits and occupational hazards that may effect the quality of sperm. In a related study, they are exposing semen samples to electromagnetic radiation from cell phones to see if an effects occur.
A British study found that cell phones may harm sperm quality in a different way. Their study found that storage of mobile phones close to the testes had a significant negative impact on the sperm concentration and the percentage of motile sperm. However, this can be avoided by carrying the cell phone somewhere other than the hip pocket or belt.
But, a study published in The British Journal of Cancer, has contrary findings. Japanese researchers looked at the effect of radiation on different parts of the brain by comparing cell phone use in 322 brain cancer patients against 683 healthy people and found "no association between mobile use and cancer," stated lead researcher Naohito Yamaguchi.
Although all findings are based on specific research samples, the implications are worth considering the next time you slip your cell phone into your belt holster.
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
 Pras Free Friends and Smile...
Pras Free Friends and Smile... Twitter Follow my tweets!
Twitter Follow my tweets! Facebook Add my facebook!!
Facebook Add my facebook!! Friendster Visit my friendster.
Friendster Visit my friendster. People String Get friend n money!
People String Get friend n money!
1 comment:
yeah.. all can be happens...
And we have to carefully every use the Cell phone.. The Radiations can effect in anyway..